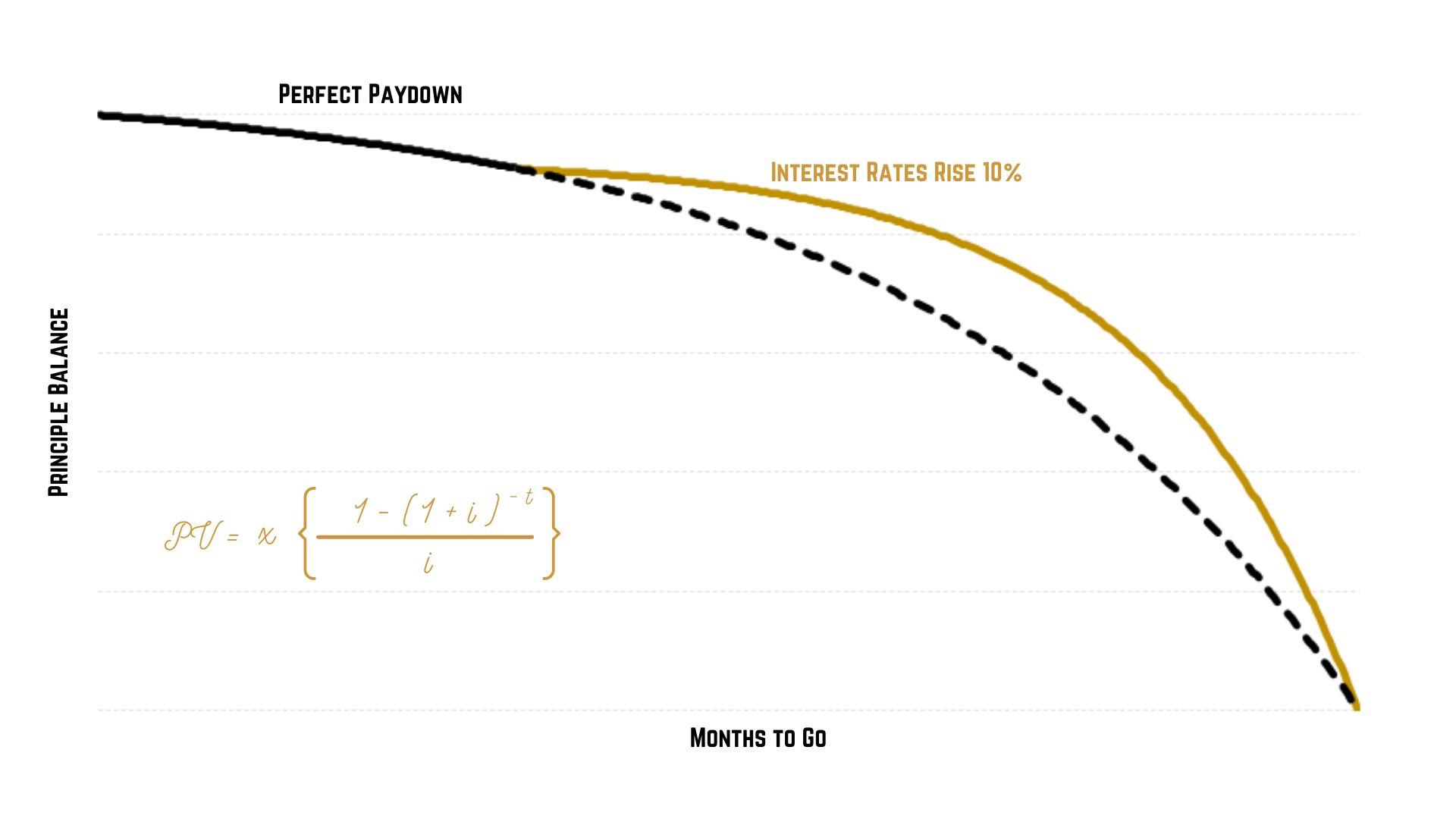
Perfect paydown curves
PV = x [ (1 – (1 + i) -t )/ i ]
Where:
PV = the present value of the loan at a given point in time
x = the instalment amount
i = the interest rate
t = the number of terms remaining
You can shuffle this all around as needed, so that: if the PV is lower than the actual balance outstanding, a customer is in arrears (in the old days I had to do this sometimes when we took on portfolios with questionable data hygiene but that’s seldom needed these days); if in collections, you need to reduce the instalment by a certain amount, you can see how many months the loan would be extended by; or, in the affordability context; if you have calculated the maximum monthly instalment and have a set term and price, what the largest affordable loan is.

